1. Acute Coronary Syndrome: This is the most serious cause of chest pain and occurs when there is a sudden blockage in one of the arteries that supply blood to the heart. It is like a dam suddenly blocking a river, causing the water to back up and potentially flood the surrounding areas. Similarly, when there is a blockage in a coronary artery, the blood supply to the heart muscle is reduced, causing chest pain or pressure. This can be a medical emergency and requires urgent attention.
Patients with ACS often have chest pain symptoms at rest, new-onset chest pain, or chest pain that is unpredictable or progressive . We refer to this type of pain as angina.Classic symptoms of angina include a squeezing, pressure-like, or heavy sensation in the chest that can radiate to the left arm, shoulder, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, lightheadedness, or palpitations.Typically these symptoms last for several minutes.Please know that older adults, women and diabetics may present with atypical symptoms without chest pain.There presenting symptom might only be fatigue, shortness of breath or palpitations.
2.Aortic Dissection: This is a rare, but potentially life-threatening condition where the inner layer of the
aorta, the largest artery in the body, tears and blood flows into the space between the layers. It can be compared to a tire blowing out, where the inner lining tears and air rushes into the space between the layers. This can cause severe chest and back pain that feels like a tearing or ripping sensation.
Patients with aortic dissection typically present with acute chest and back pain that is severe and sharp and may have a ripping or tearing quality. Pain can radiate anywhere in the chest or towards the abdomen. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, or neurological deficits.Immediate medical attention is needed to prevent further damage.
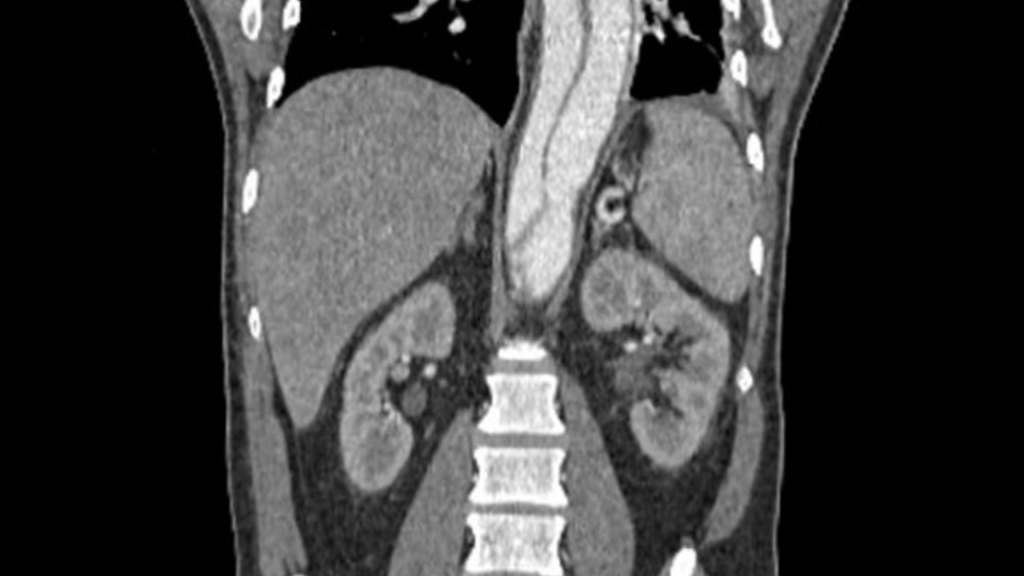
3.Pulmonary Embolism: This is a blockage of the arteries in the lungs caused by a blood clot that has traveled from another part of the body, most commonly the legs. It is like a roadblock on a highway, where traffic can no longer flow freely. In the case of a pulmonary embolism, blood flow to the lungs is obstructed, causing chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing. It is important to identify and treat a pulmonary embolism quickly to prevent further complications. Other common symptoms of pulmonary embolism include pleuritic chest pain (which just means sharp pain that worsens with breathing), rapid heart rate which manifests as palpitations, low blood pressure, sweating, or fainting.
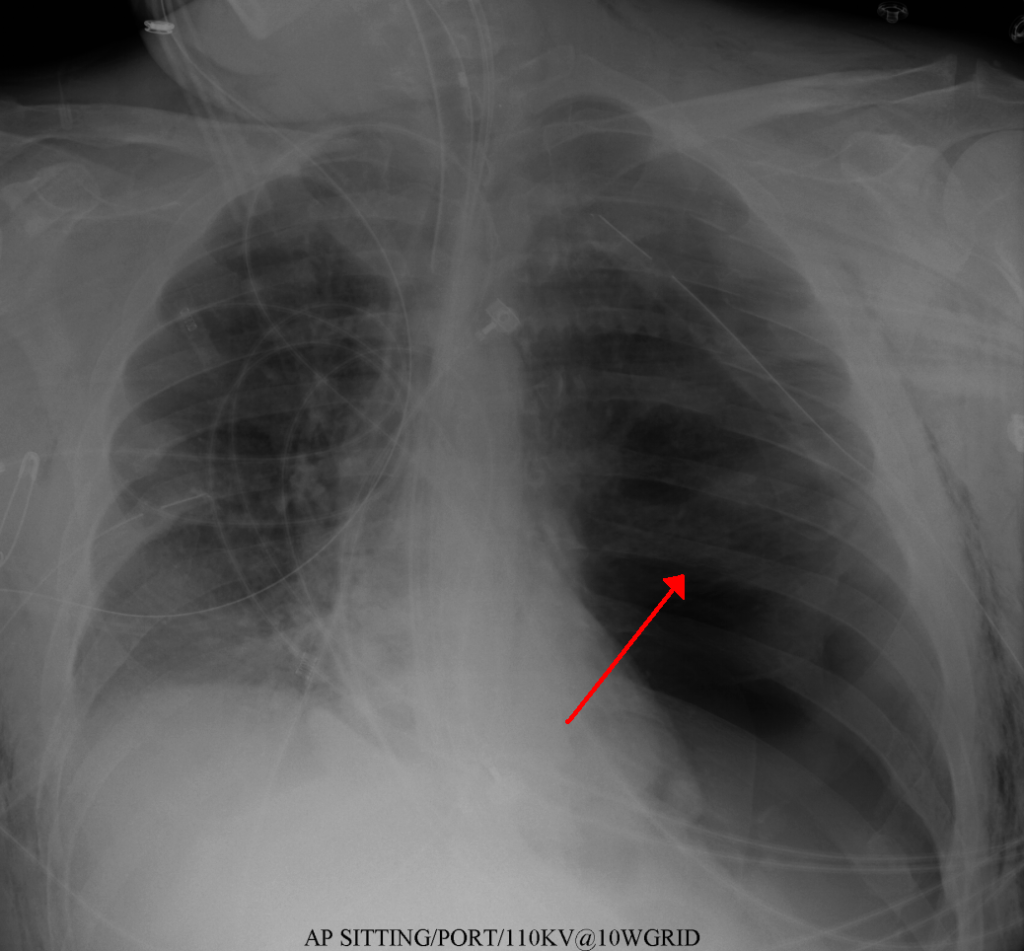
4.Tension Pneumothorax: This occurs when air gets trapped in the space between the lungs and the chest wall, causing the lung to collapse and putting pressure on the heart and other organs. It is like a balloon that has been overinflated and is about to burst. This can cause sudden onset of severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, and a rapid heart rate. Hemodynamic compromise (such as low blood pressure or a rapid heart rate) is an ominous sign and points towards impending cardiopulmonary collapse.It is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention to relieve the pressure and prevent further complications.
5.Esophageal Rupture or Perforation: This is a rare but serious condition where the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach, tears or ruptures. It can be compared to a water hose that bursts, causing water to spray out. In the case of an esophageal rupture, stomach acid and food can leak into the chest, causing severe chest pain and difficulty swallowing. Spontaneous perforation of the esophagus (Boerhaave syndrome) is caused by excessive straining or vomiting.This is seen in middle aged men who have consumed alcohol excessively or individuals with history of bulimia. Immediate medical attention is needed to prevent further damage.

6.Cardiac Tamponade: This occurs when fluid builds up in the sac surrounding the heart, putting pressure on the heart and preventing it from pumping effectively. It is like a balloon that is being squeezed, preventing air from flowing in or out. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and a rapid heart rate. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention to relieve the pressure and prevent further damage.
Sources:
🌍James Heilman, MD, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons (https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tensionpneumo.png)
CDC: https://www.cdc.gov/high-blood-pressure/
If you’re interested in other videos click right here.
Have a good day and Think your Health!






