What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin. The funny thing about vitamin D is that it behaves differently to other vitamins. In fact it is NOT really a vitamin, but rather a steroid hormone. Its chemical structure is derived from cholesterol and has similarities to sex and adrenal hormones.
The other vitamins you are aware of like A,B, C are derived from food sources.Unlike other Vitamins Vitamin D is different for the following reasons. Firstly, Vitamin D can be found in only in certain food sources such as fish or egg yolk. Although you might need only tiny amounts of Vitamin D, it must go through a series of changes to its structure before it is of benefit to you. In other words, your body makes vitamin D.
Secondly, when your skin is exposed to the sun your vitamin D is produced from cholesterol ( 7- dehydrocholesterol) in your skin cells.
So in summary you can get Vitamin D from:
- Food
- Sun
- Vitamin D which you get from food or through skin synthesis (via sunlight) is biologically inactive. It has to be transformed with the help of enzymes into its active form. These transformations chemically are referred to as hydroxylations. Two organs play an important role in this process :
- 1) your liver & 2) your kidney. The first hydroxylation takes place in your liver the second in your kidney.
- Yes, the GI tract also plays a role in calcium & phosphorous metabolism. The main function of vitamin D is to increase calcium absorption in the gut.
Vitamin D and the sun?

According to the NIH: “Some expert bodies and vitamin D researchers suggest, for example, that approximately 5–30 minutes of sun exposure, particularly between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., either daily or at least twice a week to the face, arms, hands, and legs without sunscreen usually leads to sufficient vitamin D synthesis.”
Take care when you are exposing yourself to the sun and don’t bathe in sun on hours on end without necessary sun protection. Factors which can affect your sun exposure are time of day, smog, season, cloud cover, length of day, sunscreen. Moreover, the older you are and the darker your skin the less production of Vitamin D via sun exposure. If you think you are going to cheat and try to get your sun exposure indoors through a window, that won’t work. UV-B radiation does not penetrate glass.
Why is Vitamin D so vital?

Vitamin D is important for your muscles and bones.
How does vitamin D do this?
It does this in 2 ways. One by increasing the intestinal absorption of calcium & phosphorus and in this way helping your bones stay healthier. Two it suppresses a hormone called PTH which plays a role in bone reabsorption. If you don’t have sufficient vitamin D your bones become brittle and fragile. Moreover, with the help of calcium in older adults it protects you from osteoporosis (i.e. bone loss).
Vitamin D plays a role in “normal development and growth of muscle fibers” (NIH). Therefore, if you do not take in enough vitamin D this can lead to muscle weakness and you are at an increased risk for falls.
Vitamin D has other roles as well in your body. It is anti-inflammatory, plays a role in your glucose metabolism, immune function as well as cell growth.
What causes Vitamin D deficiency?
- Lack of vitamin D in your diet- This is simple, you are not taking enough vitamin D in your diet. This is particularly true for older adults who do not take in enough vitamin D rich foods.
- If you have limited sun exposure you are at an increased risk for lack of vitamin D.
- There are certain diseases in your GI tract such as celiac disease or Crohn’s disease where the ability to absorb adequate amounts of vitamin D is reduced. Also, surgery such as gastric bypass can also lead to low vitamin D.
- I mentioned before the 2 important organs involved in Vitamin D metabolism are your liver and kidney. If you have chronic liver disease or chronic kidney disease you are at an increased risk for lower vitamin D levels.
- If you are obese that is a BMI of over 30 you are at an increased risk for decreased levels of Vitamin D. “Obesity does not affect the skin’s capacity to synthesize vitamin D. “However, greater amounts of subcutaneous fat sequester more of the vitamin”.
What happens if you are Vitamin D deficient?
In children you develop a bone disease called rickets. This disease makes the bones softer and the bones are more prone to fractures and deformities. In adults you have something similar where your bones become softer bones as well as weaker.This condition is called osteomalacia because the bones are not completely mineralized causing bone pain, deformities and in severe cases lack of vitamin D causes decreased calcium you are at an increased risk for seizures.
When you get older you are at a risk for osteoporosis. This in contrast to osteomalacia can result from the lack of vitamin D and or lack of calcium. Osteomalacia is secondary to lack of vitamin D. As already mentioned earlier, esp. in older adults’ lack of Vitamin D can lead to poor bone health and muscle health and you would be at an increased risk for falls.
What are the main symptoms of Vitamin D deficiency?
Here are & 8 signs and symptoms:
- Fatigue and feeling tired, some individuals complain of low energy
- Bone pain coupled with lower back pain
- Mood changes: feeling down & depressed
- Delayed wound healing ( watch out if you are a diabetic!)
- Hair thinning & hair loss
- Increased risk of infections (observational studies have noted an associated with cold, bronchitis & even chest infection)
- Bone loss (Osteoporosis)
- Muscle weakness & pain
Sources of Vitamin D:
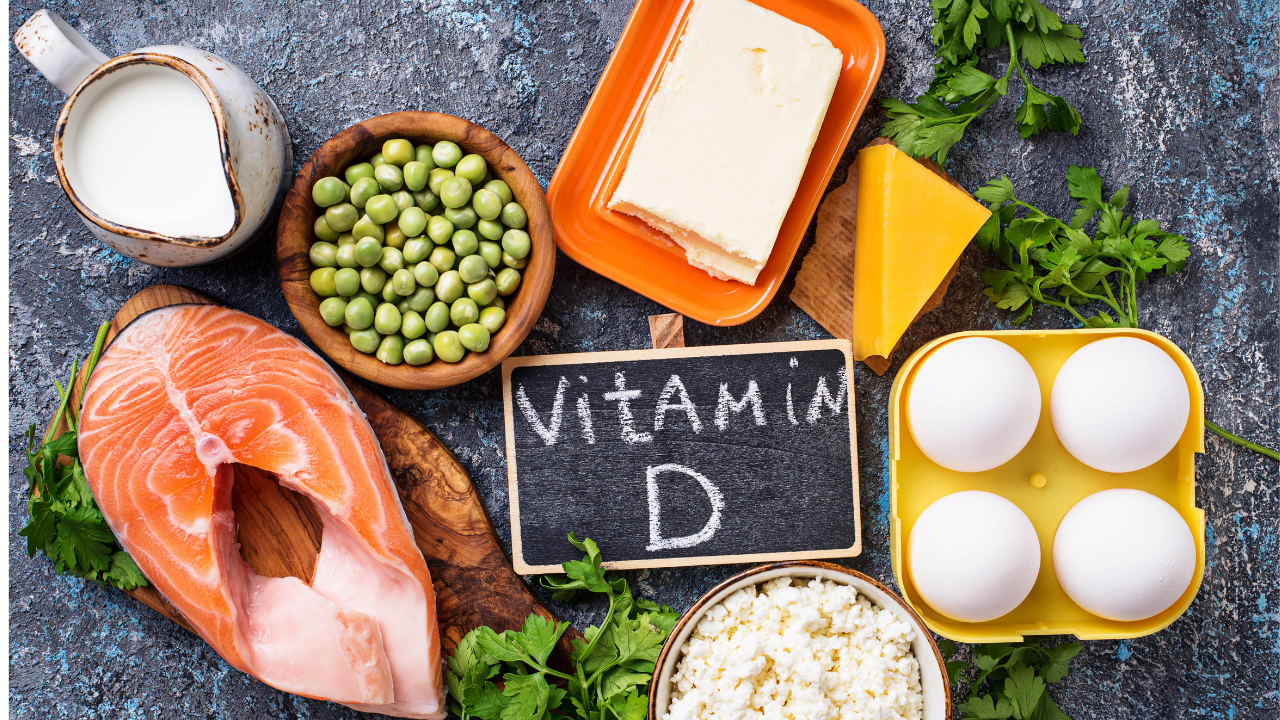

Perhaps I should start off with there are 2 forms of vitamin D, D2 & D3. Vitamin D2 is found in plants and yeast while Vitamin D3 is primarily seen in animal sources. D2 is also referred to as ergocalciferol and D3 as cholecalciferol. Both types will raise your Vitamin D levels.
The recommended dietary allowance as stipulated by the NIH is for ages 19 and above 600 IU of vitamin daily and above the age of >70 800IU of Vitamin D daily.
Best sources of vitamin D would be fatty fish. Examples would be salmon, mackerel, tuna or trout. Other animal sources include egg yolks, cheese, as well as beef liver. Mushrooms are a good source of Vitamin D2. Also for example here in the US milk is fortified with Vitamin D.( About 3mcg/cup which translates to about 120IU of Vitamin D).Other products such as Orange juice, yogurt or even breakfast cereals are also fortified with vitamin D.
Here are some examples:
- 3 ounces of salmon cooked is 570 IU/serving of Vitamin D,
- 3 ounces of chicken breast roasted is 4IU/serving,
- cod liver oil one tablespoon is 1,360 IU/ serving
- or ½ cup of raw white mushrooms is 366 IU/ serving.
How to diagnose Vitamin D deficiency?

- This can be done with a simple blood test. These are values from the National Academy of Medicine.
- A normal value is defined a vitamin D concentration as greater than 20 ng/ml. Mind you there are some labs which use 30 ng/mL as the cut off.
- You are seen as deficient if your value is less than 12 ng/mL. You are insufficient if your value is 12-20 ng/mL.
How to treat Vitamin D deficiency?

You can supplement with Vitamin D2 or Vitamin D3. You can supplement with both but most experts recommend Vitamin D3 as it can raise levels more effectively.
If you are Vitamin D deficient supplementation is as follows:
50,000 IU of Vitamin D2 or D3 weekly ( or twice a week) for about 6-8 weeks and then 1000 IU of Vitamin D3 daily. Now if there is a compliance issue or you have too many pills you can continue with 50,000 IU monthly.
If you are Vitamin D insufficient:If your level is between (20-30 ng/mL) you can get supplemented in the following way: 600-800 IU of Vitamin D3 daily to reach your target level.
While taking in Vitamin D it is recommended to take 1000 mg daily of calcium for premenopausal women and men , and for post-menopausal women 1200 mg daily.
Once you have started treatment you can get a follow up Vitamin D level about 12 weeks after initiating treatment.
QUESTION OF THE DAY?
How much Vitamin are you on and what is your Vitamin D level?
Here are some medications which can interact with Vitamin D.If you are on these medications are your vitamin D levels are not at target you can talk to your health care provider about possible interaction:
Statins, Steroids, Thiazide diuretics, Orlistat
Can you take in too much Vitamin D?
If you take in an excess of Vitamin D, this is referred to as hypervitaminosis D. Taking in too much Vitamin D leads to excess calcium in your blood. This condition is seen rarely seen. This is not caused by excess sunlight or food, rather if you take in excessive supplements.
Your main symptoms of toxicity would be GI symptoms: nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and poor appetite. You will also feel tired and weak and urinate frequently. In severe cases this can lead to kidney failure and bone loss.
If you are interested in other videos, click right here.Have a good day and think your health!
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-side-effects#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/