Are you a diabetic? In this article we will look at screening tests and evaluation needed to avoid complications of uncontrolled diabetes.
1 – Eye complications:

You are at an increased risk for cataracts, glaucoma, and vision loss. Another complication you want to avoid is diabetic retinopathy where you can have smaller bleeds in your eye. General measures to reduce risk and progression of retinopathy include good blood sugar and blood pressure control. I would recommend that you have an eye examination at least yearly with your eye Doctor.
2 – Cardiovascular complications:

Both men & women are at risk from developing and dying from these complications. Your life expectancy can be reduced by as much as 6-8 years. I am sure you don’t want that and want to continue to enjoy a reasonable quality of life. Many patients with type 2 DM have other risk factors and markers of cardiovascular disease such as obesity, high blood pressure, and high bad cholesterol. Another huge risk factor is smoking.
How can we manage these risk factors?
- If you are a diabetic and are a smoker. The most important thing that you can do to take control of your health is to reduce and better yet quit smoking.
- You can take Aspirin daily and the recommended daily amount is 75mg to 162mg, depending on which country you live in, here in the US it is 81mg daily. Now, this is recommended for you if you have an increased cardiovascular risk. Who are these people? If you have PVD, have had a heart attack, bypass or a stroke or a mini stroke. If you do take ASA daily, you do have a slightly increased chance of a GI bleed. In certain individuals the risks might outweigh the benefits, for example if you had a GI bleed in the past. If your cardiovascular risk is low (you can have that discussion with your Doctor), it is routinely not recommended.
- Blood pressure control is important in diabetes. It is especially important to decrease the progression to diabetic kidney and eye disease called diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy. Your goal treatment should be at least to have your systolic blood pressure to be less than 140mmHg and your diastolic blood pressure to be 90mmHg.If you have a lot of cardiovascular risk factors the AHA recommends your goal blood pressure to be at less than 130/80 mmHg. You must remember these goals are general guidelines. The older you get; I do expect your blood pressure to go up. You can have this discussion with your Doctor what your target BP should be.
- Dyslipidemia— If you are a diabetic, it is not unusual also to have abnormalities with your lipid panel. The most important measure you can do to improve these abnormalities in your lipid panel is diet, exercise, and weight loss. Typically, a Statin drug is added if you have abnormalities with cardiovascular risk factors. If you have been following my articles, I always encourage a non-pharmacological approach to control you elevated cholesterol. You must weigh in the pros and cons if Statin therapy is initiated. Especially, if you are an older adult the risks might outweigh the benefits.
- Another staple of managing your Diabetes are diabetes medications. Now there are too many to talk about and would require a video series to discuss. Some of these medications would include Metformin, a group of diabetic medications called GLP-1 Receptor agonist and SGL2 inhibitors.
3 – Foot complications:
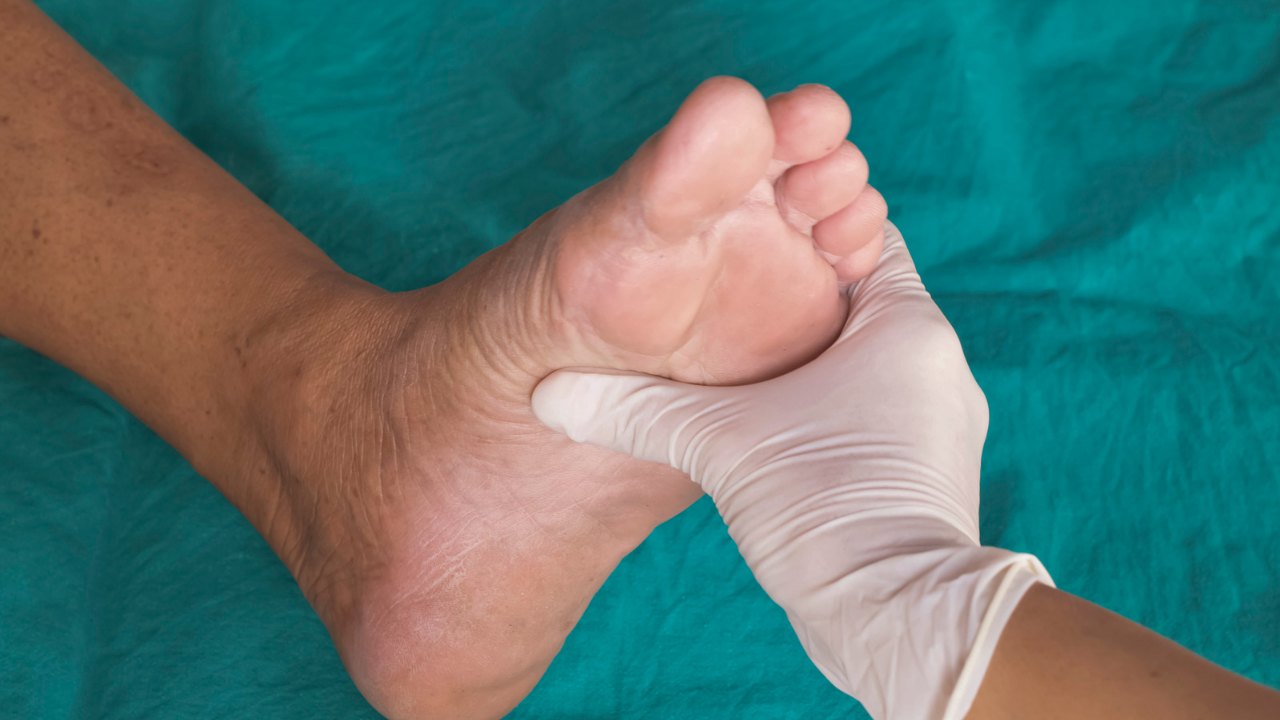
At every exam your Doctor should look at your feet. They should check your feet palpating your pulses and checking the sensation of your feet checking for signs of diabetic neuropathy. Moreover, the foot exam serves to check for callus formation, fungal and wound infections as well checking for ulcers. Appropriate footwear should be discussed as well as foot and nail hygiene discussed. If your Doctor believes you have problems with blood perfusion, they will order a test called arterial dopplers to measure your ABI ratio. An ABI ratio between 1.0 and 1.4 is normal. An ABI ratio between 0.9 and 1.0 is borderline. An ABI ratio of 0.9 or less means you have PAD. An ABI ratio between 0.5 and 0.8 means you have moderate PAD. If your ABI ratio is less than 05 than you have severe PAD.
4 – Kidney complications:
Diabetes can harm your kidneys. This is because the blood vessels in your kidneys as well as the tiny blood vessels supplying the filtering units of your kidneys become damaged. Overtime, because of high blood sugars these vessels become narrower and clog up. Your doctor with a blood test can check your renal parameters as well as checking your urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio. The normal rate of albumin excretion is less than 30 mg/day If your value is more than this (30-300 mg day) this might be indicative of damage to your kidneys and we refer to this as diabetic nephropathy. If the value is more than 300mg/day this is indicative of damage to the kidneys, and we describe this state as proteinuria.
5 – I would recommend at least a yearly examination with your dentist. As a diabetic you are more prone to infection and if you do have gum disease it is more severe.
6 – These vaccinations are recommended for diabetes:
- Influenza vaccination yearly, with or without diabetes
- Pneumococcal vaccination, per US Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) protocol, with one pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) in adults ≥65 years and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) once before and once after age 65.
- Hep B
These are the recommended studies for you to have checked routinely.
These would include: HbA1c, lipid panel, Serum creatinine, urinary albumin creatinine ratio
Think your Health and have a good day.You can watch the entire video here.
Sources:





