What are gallstones?
Gallstones are solid, pebble-like material that form inside the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a sac like organ located under the liver. Gallstones can be the size of a grain of sand or even as large as a golf ball.(woo that must be painful, imagine that sitting in your gallbladder.!) Luckily, the majority of gallstones are smaller than 1 inch (which is about 2.5 cm in size).80% of gallstones are cholesterol gallstones, the other 20% are Pigment stones.
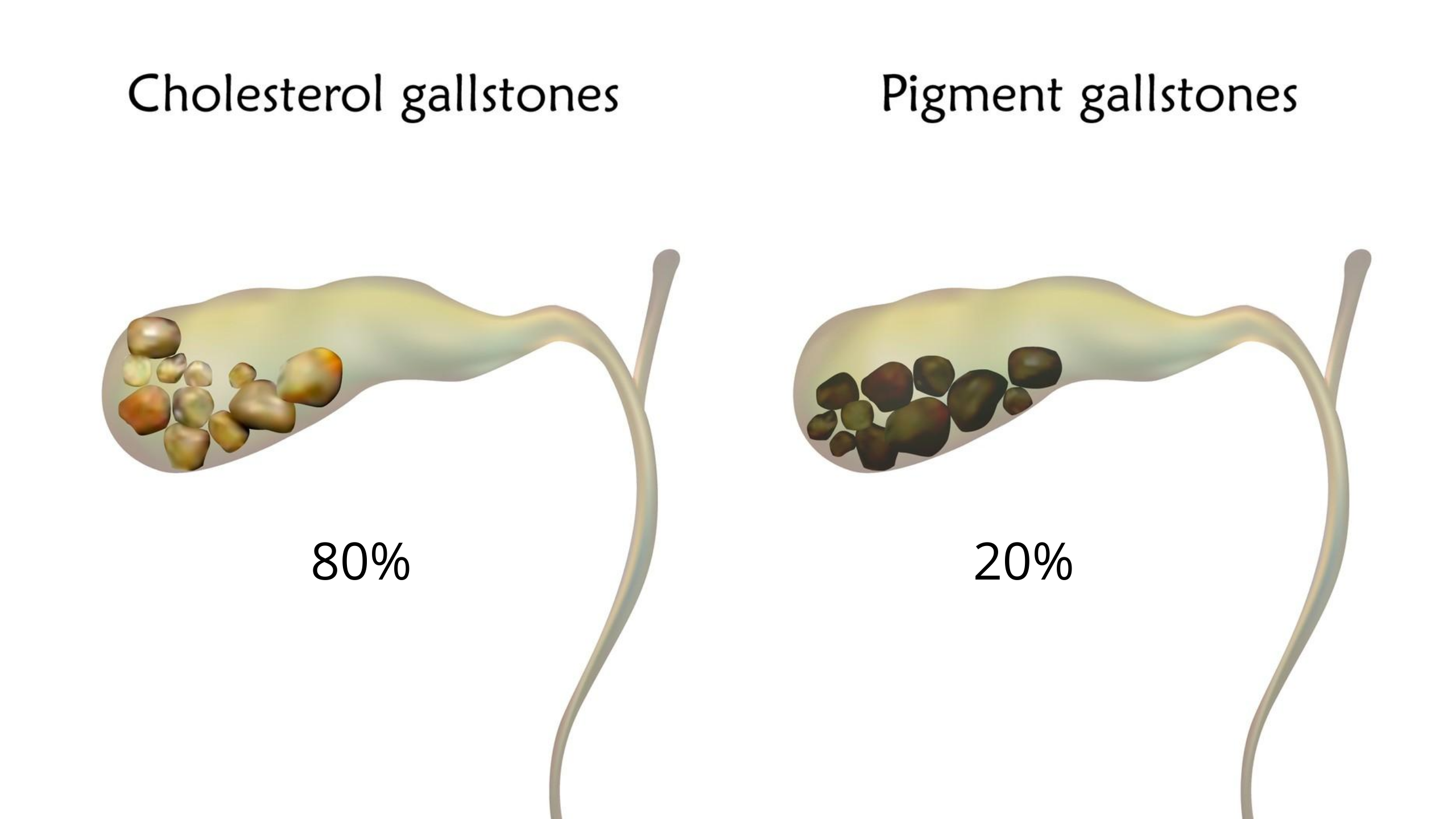
What causes gallstones?
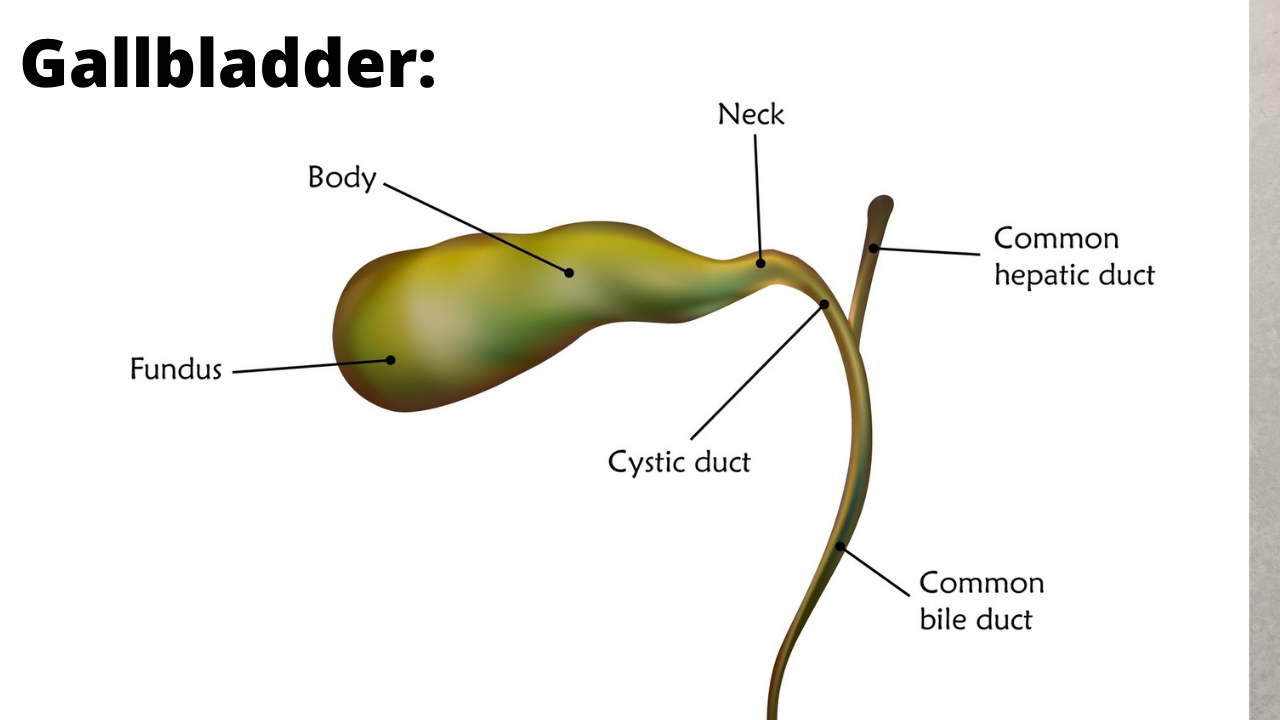
The liver makes and releases bile. Bile is stored in the gallbladder. Bile is a greenish-brown fluid, and the gallbladder not only stores it, but also concentrates the bile. When we eat a meal, let’s say something fatty (like good old cheeseburger with cheese dripping down the side), the gallbladder says I need to do something about this and gets active and contracts and bile flows from the gallbladder to our small intestine to help with digestion. In between meals the gallbladder is relaxed allowing bile to flow into the gallbladder. Now, if there is too much cholesterol, or too much of another substance called bilirubin or not enough bile salts gallstones may form. Also, if the gallbladder does not empty completely or often enough gallstones can form.
How many people are affected in the US by gallstones?
On a yearly bases more than a million Americans are diagnosed with gallstones. Your physician might use the term cholelithiasis.
Check YouTube video: here.
Are you at risk for gallbladder stones? These are the risk factors:
- Have a family history of them
- Are a woman
- Are over age 40
- Family history and genetics
- Are obese or morbidly obese
- If your diet is high in fat but low in fiber
- Frequently fasting
- Rapid weight loss
- Or for that matter lack of exercise
- Use birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy.
- Are pregnant
- Have diabetes
- Have hemolytic anemia such as sickle cell disease
- Cirrhosis of the liver
What are gallbladder stone symptoms?
The classical symptoms are having pain after eating a fatty meal. You have abdominal pain located classically in the upper right side of your belly, with radiation to your right shoulder or to your back. You might be vomiting or feel nauseous. Some people present without having eaten anything with pain usually around midnight.
Having said that many people have silent gallstones, meaning they are found incidentally during a CT scan or an Ultrasound. If the stones are not symptomatic, they do not need treatment and can be monitored by your provider.
How to diagnose gallstones?
- Most important initial test would be an examination by your provider coupled with specific blood tests to rules out signs of infection as well as blockage.
- The next test would be an Ultrasound, which is a non-invasive test looking at your gallbladder which can pick up stones. Most of the time a diagnosis can be established by these tests.
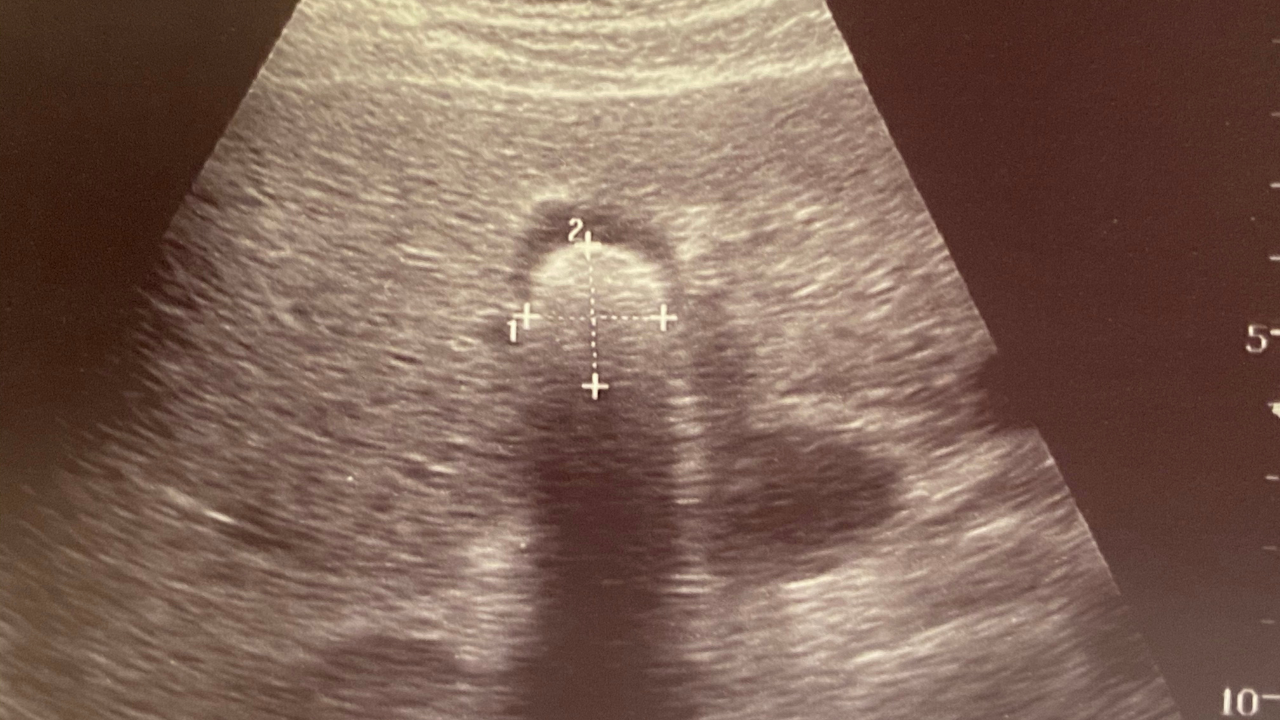
- However, if the diagnosis is not conclusive your doctor might order a CT scan to get a more detailed view of the GB, liver and bile ducts.
- Your doctor might order a test called a HIDA scan especially if the gallbladder is acutely infected coupled with a blockage of the gallbladder outlet. It is also used to look at gallbladder disease without any stones known as acalculous cholecystitis.
- Then there are 2 more specialized tests one called MRCP and ERCP specially to look at gallbladder stones blocking the bile ducts. During an ERCP the added advantage is not only diagnosing a gallbladder stone in the bile duct but also removing it.
Gallbladder stone complications:
- If the gallbladder becomes blocked by a stone or stones it causes an inflammation of the gallbladder. This presents as pain which is constant, especially in the right upper side of your belly.
- Fever is common. Older adults can present atypically without a fever and sometimes even without pain. If not treated this can lead to a rupture of the gallbladder which is an acute medical emergency.
- If stones leave the gallbladder and cause a blockage of the bile ducts it is called called choledocholithiasis.
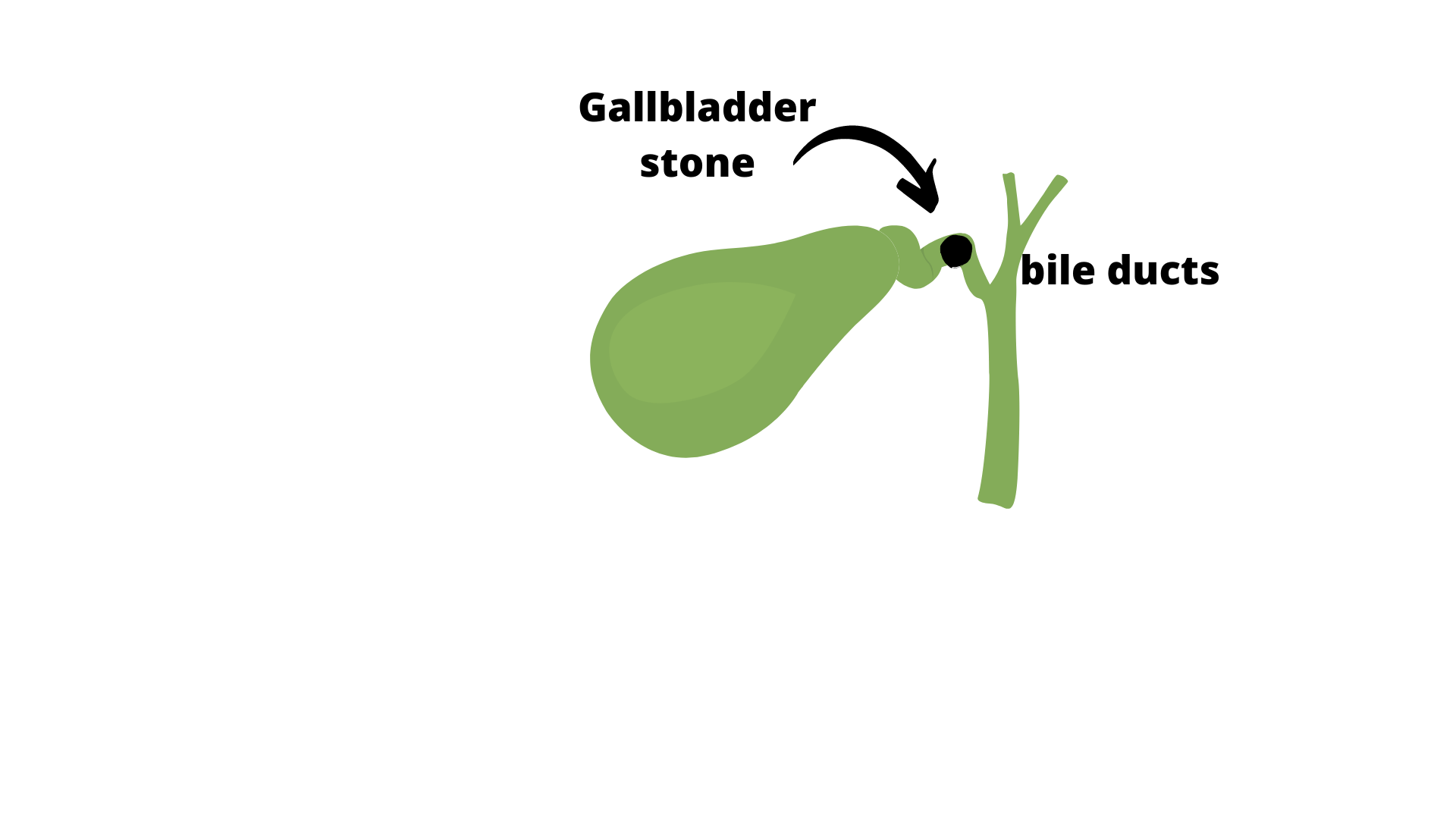

Typical symptoms are fever, abdominal pain, chills, as well as jaundice: that is a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the white of the eyes. It can also cause an inflammation of the pancreas. This is another medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to remove the blocked stone or stones by means of an ERCP.
How do we treat gallbladder stones?
- If you don’t have any symptoms, you do not have to be treated. Your doctor would monitor you and give you advice about diet, hydration, and lifestyle changes. Some small gallstones can pass through your body on their own.
- If the stones continue to be symptomatic and cause problems your doctor might offer one of 2 options:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy which is the most common surgery for gallstones. Through a small cut in your belly your doctor passes a narrow tube called a laparoscope. It holds a camera and light. During the procedure your gallbladder is taken out through another small cut. Usually, you can be discharged back home that very day.
- The other surgical procedure requires you to stay in the hospital for a couple of days. During this procedure called an open cholecystectomy the gallbladder is removed using a bigger cut in your belly.
- As I mentioned earlier if gallstones are in your bile ducts, your doctor may use a procedure called ERCP to find and remove the gallbladder stones before or even during surgery.
- Non-surgical treatments are usually offered if the risks of surgery are too high. The disadvantage with this option is that the stones can recur after some time.
- You doctor might use a bile acid pill to dissolve cholesterol stones called Ursodiol. A side effect of the medication is diarrhea. You will have to be on this medication for several years as it takes years to dissolve the stones.
How can you prevent a recurrence of gallbladder stones and problems?
Your diet should include the following:
- Low-fat dairy foods.
- Whole grains, such as brown rice, bran cereal, oats, whole wheat bread and whole wheat pasta.
- Lean meats and poultry.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
You should avoid:
- Fried foods.
- Highly processed foods (doughnuts, pie, cookies)
- Whole-milk dairy products (cheese, ice cream, butter)
- Fatty red meat.
Exercise regularly, about 30 minutes 5x a week
Have a good day and Think your health! Check entire YouTube video here.
Sources:
1)https://www.uptodate.com/contents/





