Blood in the urine, what does it mean (Hematuria): Doctor examines 10 causes!
Do you have blood in the urine, are you wondering what is causing the blood?
This article will look at 10 causes of blood in the urine.
You have blood in your urine ………should you be worried?
Is blood in the urine serious?
If you see blood in your urine, it can be quite scary? All kinds of thoughts are racing through your mind! Is it cancer? Am I going to die? What should I do? The medical term for blood in the urine is called “hematuria”. You should follow up with your Doctor for a workup. For the most part it is something less serious, however, you do want to exclude something bad going on with your body.
Where is this blood coming from?
Blood in the urine can come from the kidneys (where urine is made) or anywhere in the urinary tract which includes the ureter, bladder, and urethra.
How do I know it is blood?
Well, your pee is usually a pale-yellow color. If there is blood in it your pee turns pinkish, brown, or even red. This is easy to see with your own eyes. Other times your Doctor might say that you have blood in your urine in a lab test although you can’t see blood with your naked eye.
What are 10 common causes for blood in the urine?
What does blood in the urine indicate?
1. Urinary tract infection, bladder, or kidney infection
2. Kidney stones or bladder stones
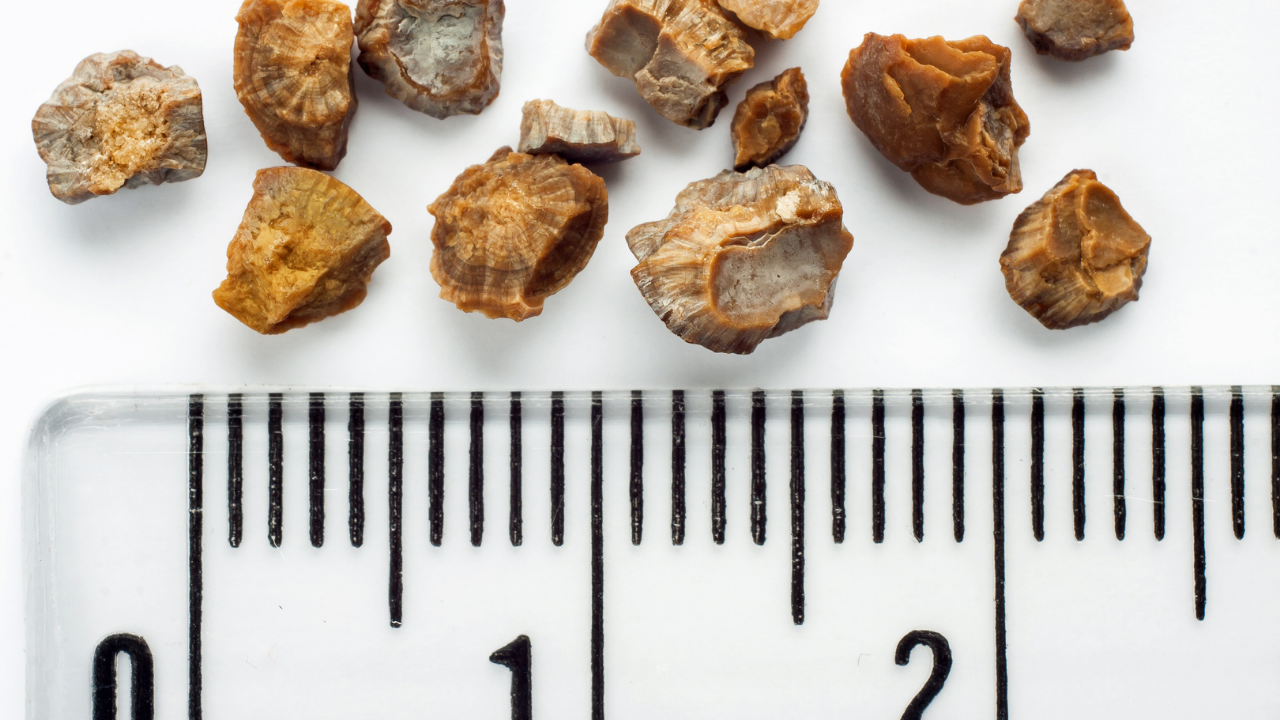

3. A kidney disease called glomerulonephritis
4. Cancer of the kidney, bladder, or prostate (usually people are older, above the age of 50)
5. Injury or trauma to the kidney like a sport injury when the kidney is bruised
6. Enlarged prostate, also called BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia)
7. Vigorous exercise
8. Medications, usually blood thinners such as Aspirin, heparin, the anti-cancer drug called cyclophosphamide and the antibiotic penicillin
9. Inherited disorders such as sickle cell disease and cystic kidney disease
10. Blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia
BONUS FACT: Eating beets, blackberries or even food coloring can make your urine reddish, but this is not blood.
Check YouTube video blood in the urine:
Blood in your urine: How to diagnose and what is the work-up?
- A physical examination as well as good medical history is needed.
- Your Doctor will order a test called urinalysis to look for red blood cells.
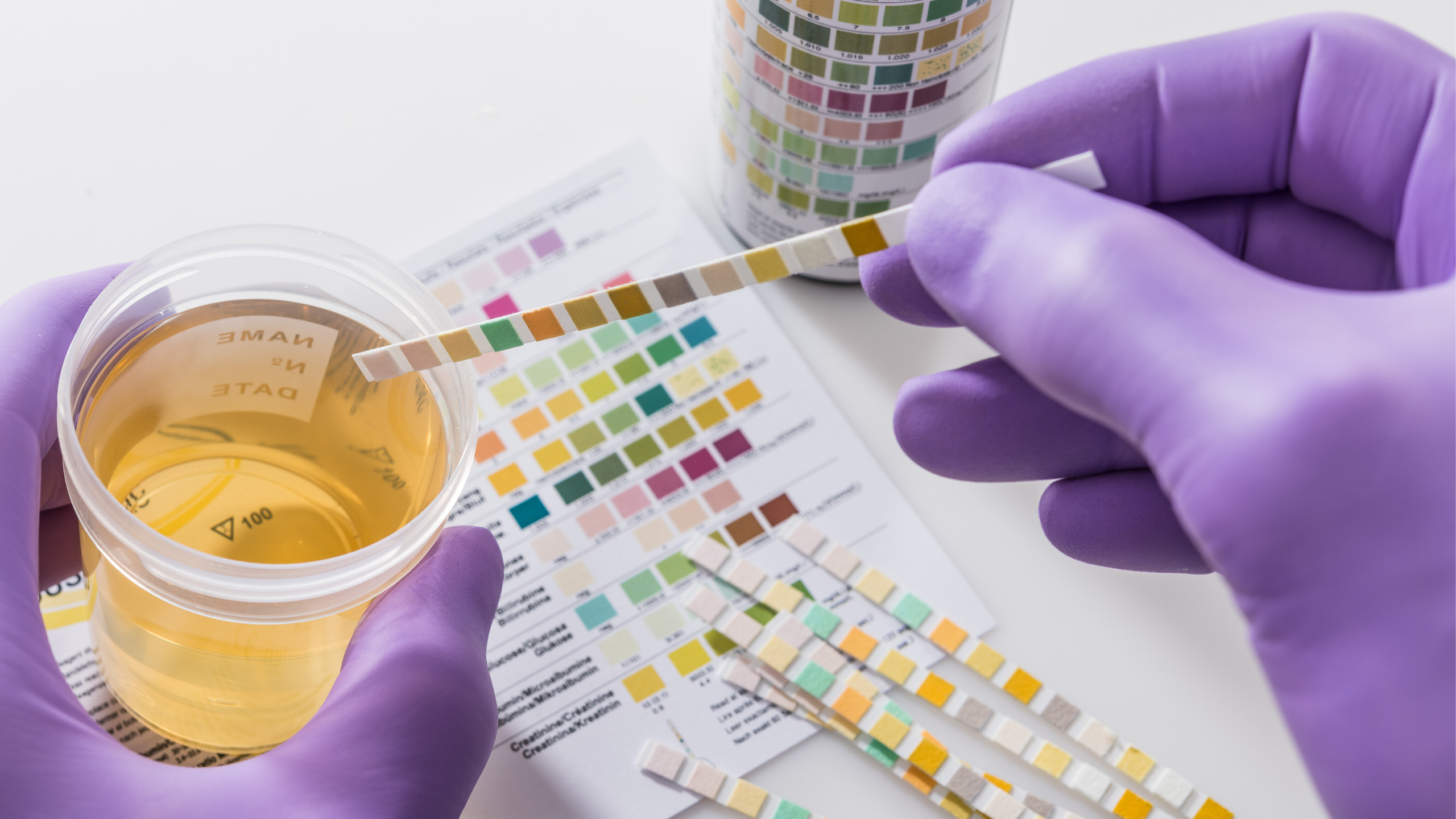
- If he or she suspects her UTI they might order a urine culture as well.
- Another urine test would be urine cytology which analyses the cells from the lining of the bladder and the kidney underneath a microscope.
- Blood tests can be ordered to look at kidney parameters to diagnose kidney disease.
- A kidney ultrasound to look at kidney anatomy and structure.
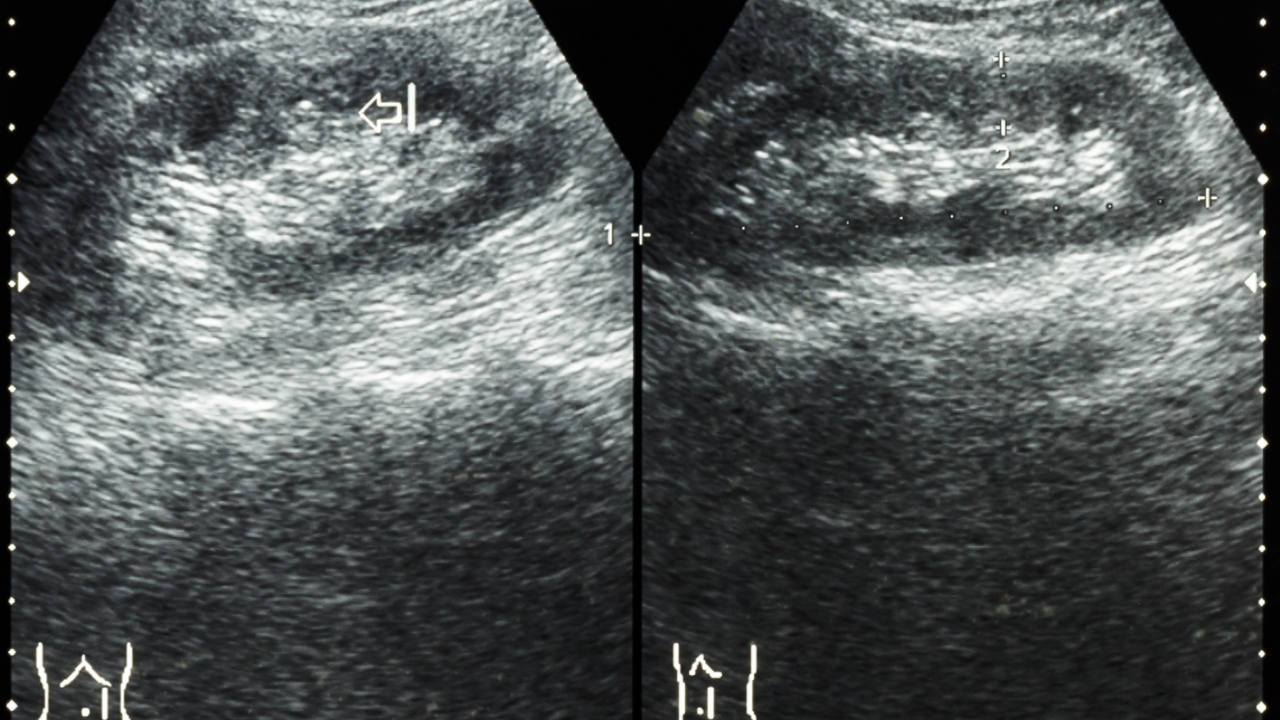
- A more involved test would be a CT scan. Usually, a dye Is injected to look for any abnormalities in the urinary tract also including the kidneys.
- Another procedure would be a cystoscopy. A small tube with a camera is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. This can be done in the office setting, however, quite often it’s a one-day surgical procedure. During this procedure the surgeon looks at the inner lining of the bladder.
For a definite diagnosis (esp. if cancer is suspected) a kidney biopsy is required. This involves removing a small piece of tissue from the kidney which can be later studied under the microscope.
Treatment:
The treatment would depend on the underlying cause of the hematuria. If it is a UTI your Doctor will ask you to hydrate well and place you on an antibiotic. If it is a kidney stone, he or she choose a specific treatment depending on the size of the stone.
Also depending on test results you Doctor might opt to send you to a urologist or nephrologist.
Have a good day and Think your Health. You can see the entire YouTube video here:
Sources:
1) https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/
2) https://www.uptodate.com/contents/