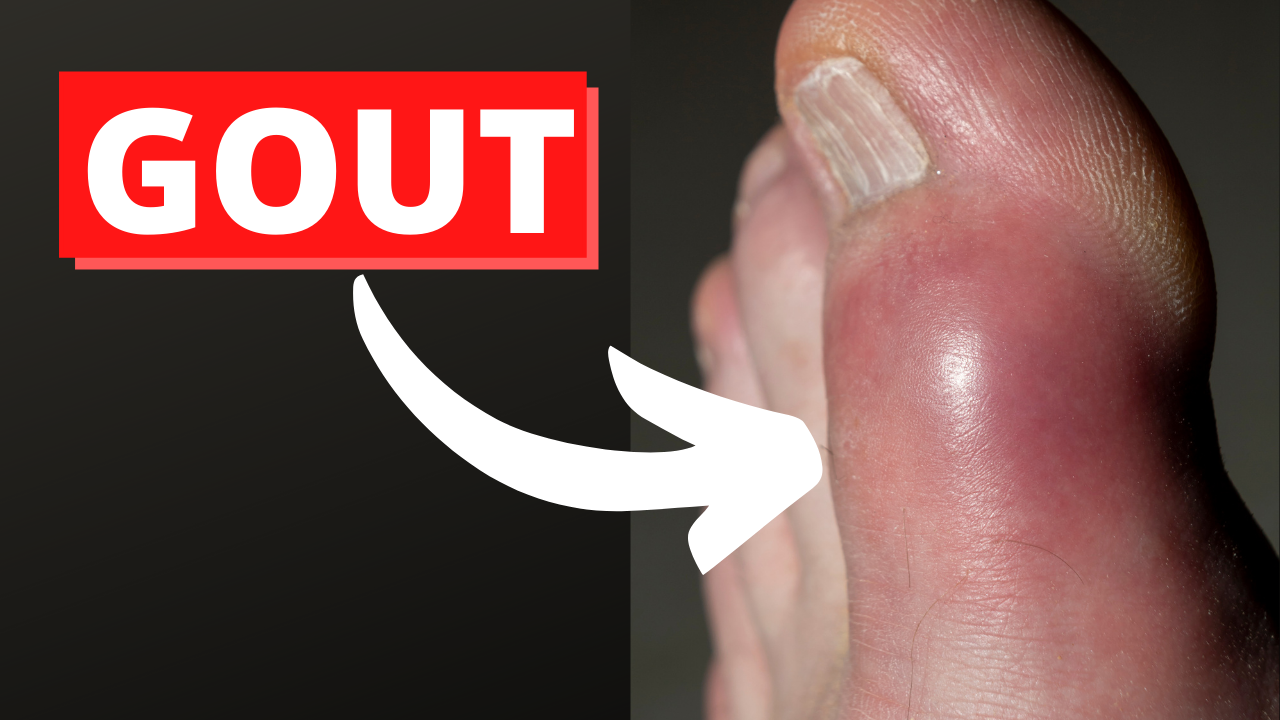
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis. It is caused by increased levels of uric acid in your blood.
Uric acid is formed when your body breaks down purines. Purines are substances found in your animal and plant foods. When you have too much uric acid in your blood, your kidney is not able to get rid of it. This condition is also called hyperuricemia. This causes crystals of uric acid to form and build up in your joints. It usually tends to affect your big toe joint.
As the disease progresses, other joints can be involved. The accumulation of these crystals causes pain and swelling in the affected joints.If these crystals build up in the smaller tubes of your kidney, they can form kidney stones and cause an obstruction in the flow of your urine.
What are typical gout symptoms?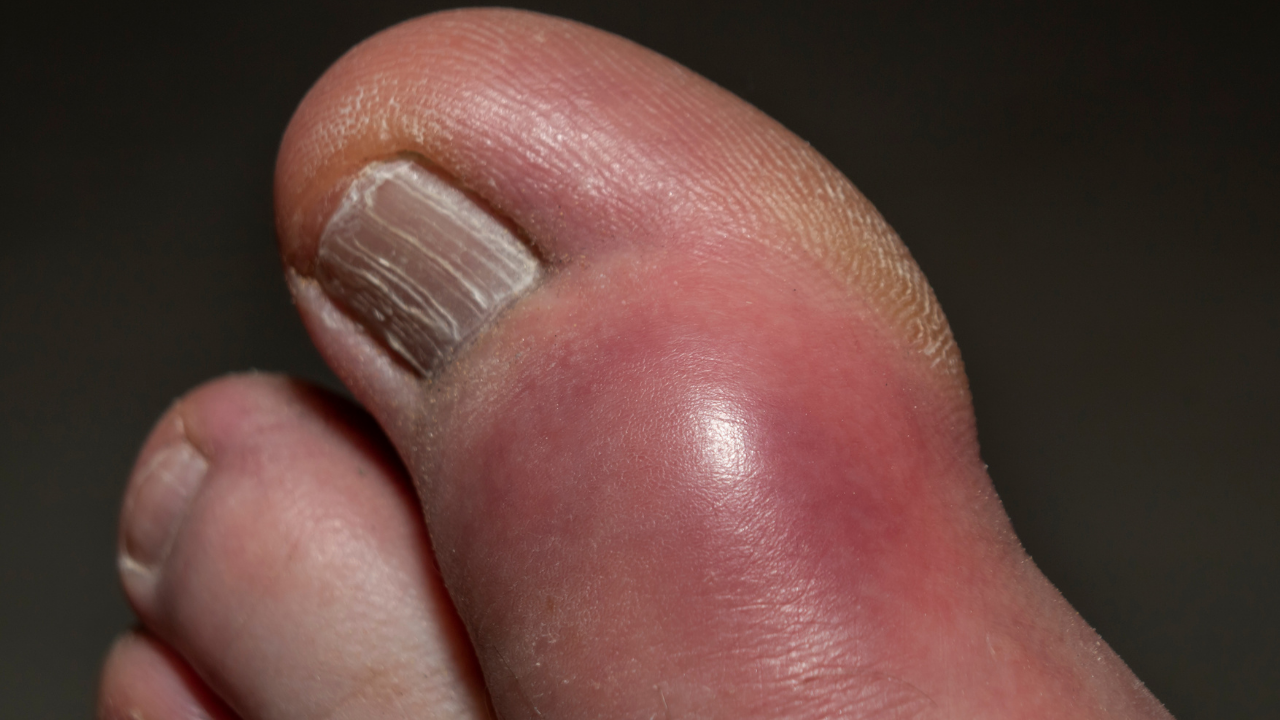
You will experience pain, redness and swelling of the affected joint. These gout attacks come on suddenly. Most often they start at nighttime or even in the early morning hours. They can, however, start any time of the day.
Classically, your big toe gets affected. Some individuals can have several joints which are affected. Your pain can increase with intensity and reaches its peak within 12-24 hours. In the next couple of days and sometimes weeks your pain should improve.
The reason you have pain is because your body sees these crystals as foreign bodies and an inflammatory reaction is set off to get rid of these foreign bodies. These chemical cascades release several substances causing redness, pain and swelling in your joint or joints. Initially, if you have a gout attack it only involves a single joint. Overtime, especially if your gout goes untreated multiple joints can be involved.The joints affected can be your knees, toe joints and ankles. Between the gout attacks you can have longer periods of no symptoms and these can last weeks, months and even years. The problem that can arise is that if your gout goes untreated over several years not only will the time between gout attacks shorten, however, several joints can be involved.
What happens if you have a longstanding history of high uric acid? (Hyperuricemia)
You develop a form of gout called tophaceous gout. In this form of gout, uric acid crystals in masses also called “tophi” accumulate in various areas of your body including in multiple joints, tissues, bones, cartilage and even under the skin. Under the skin they look like nodules. Tophi can cause damage to your bones and cartilage resulting in deformities of your joints.
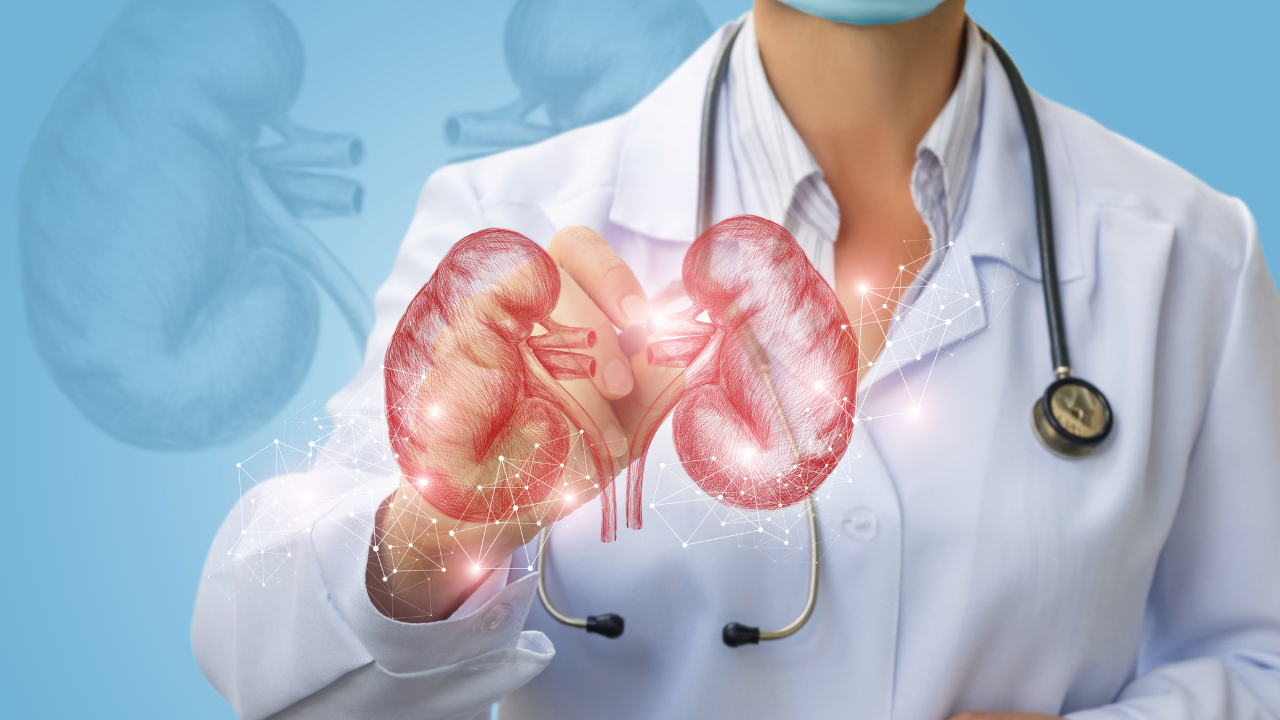
What happens to your kidney if you have gout?
You can have an accumulation of urate crystals which build up in your kidney or even in the urinary tract. This leads to the formation of kidney stones. This can lead to an obstruction of the ureter (which are the tubes which lead from the kidney to the bladder).
What are the risk factors of gout?
- These include obesity
- HTN
- Diabetes
- Congestive heart failure
- Poor kidney function (chronic kidney disease)
- Using medications such as water pills (HCTZ, LASIX)
- Drinking alcohol regularly & excessively
- Having a diet high in purine rich foods. Here you will see listed some of them and by no means is this list exhaustive….. Especially Alcohol, sweetened drinks, high fat (fried food, full fat diary, rich deserts), wild game such as duck or venison, organ meat such as liver or kidneys, some seafood such as tuna, sardines, herring, red meat.
- Consuming large amounts high fructose syrup in the form of drinks or food
- Prolonged fasting
- Eating large amounts of meat and seafood (sardines, trout, tuna). These purine rich foods which the body beaks down into uric acid
How is Gout diagnosed?
This requires a thorough history and physical examination by your health care provider including a detailed look and you’re eating and drinking habits as well as studying your medication list.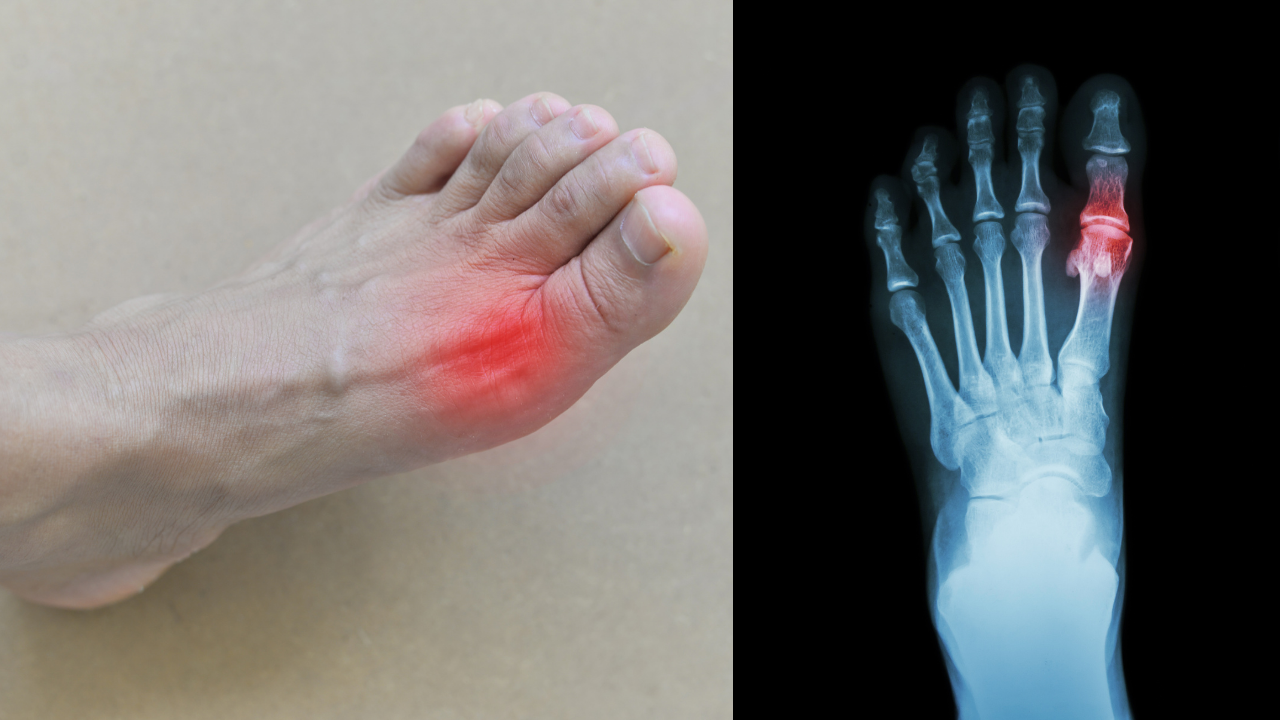
Other tests which can be done are x-rays as well as lab tests looking at uric acid levels. Having said that a uric acid level during a gout flare up is difficult to interpret as the level during an acute attack can be low, normal, or high. It is more diagnostic two or more weeks after a gout attack. Other blood values which can be elevated are ESR and CRP.
The most accurate diagnosis would be examining the fluid in your joint. Your health care provider will remove small amount of fluid from inside your joint using a needle and syringe under aseptic conditions. Urate crystals can be then examined under the microscope.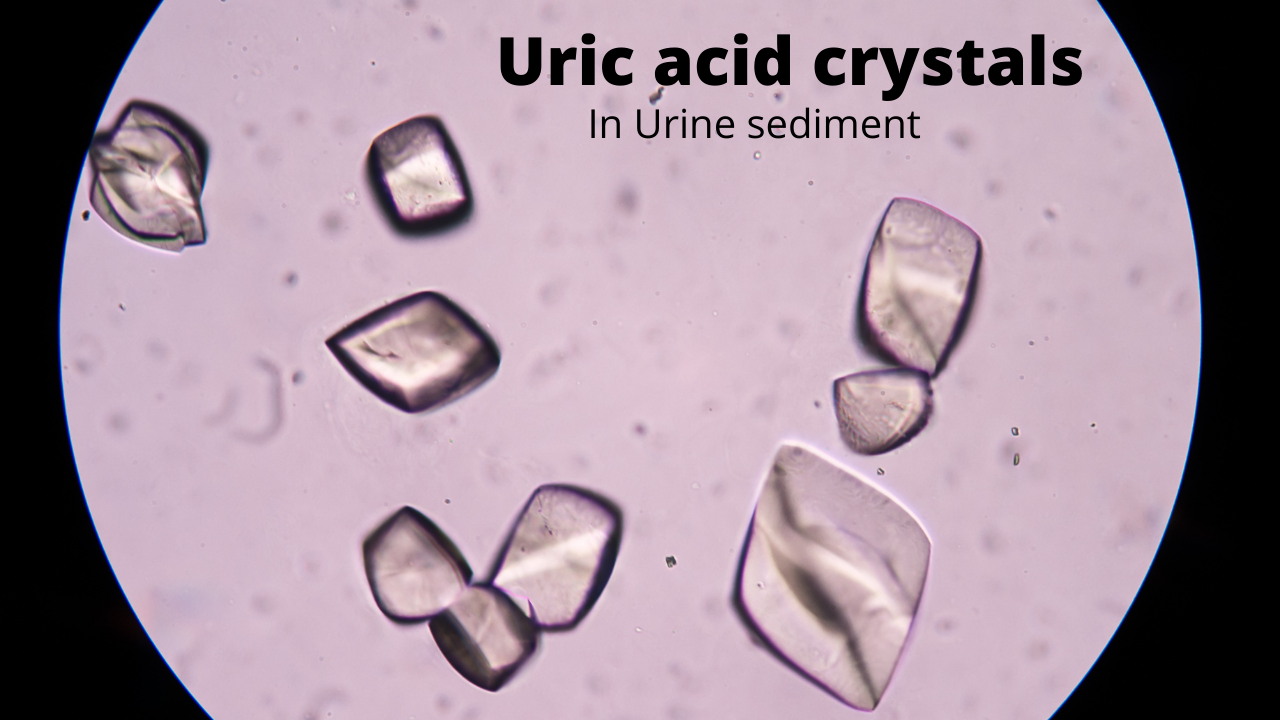
- What is the fastest way to get rid of gout?
- What is the drug of choice for gout?
Choice of medication will depend on several factors including your previous history and treatment of gout, your kidney function, bleeding history and history of stomach ulcers.
NSAIDS such as Ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, or celecoxib are used as anti-inflammatory medications to reduce the swelling of the joint. They are most effective the earlier they are started during a gout attack.
However, NSAIDS are generally not recommended in older adults given the side effects of these medications. NSAIDS are also not recommended if one of these applies to you: on blood thinners (like warfarin), bleeding history, stomach ulcers, liver, or kidney disease.
Another medication which can be used instead is Colchicine. This medication should be started within 24 hours of a gout attack. The dosing is different if you are using Colchicine for an acute attack or for prophylaxis:
During an acute attack your health care provider can start you on 1.2mg followed by 0.6mg after one hour. Other health care providers prefer to give the medication three times a day during an acute attack. The dosing would be 0.6mg three times daily. The worst pain is on that first day and this can be followed on day 2 by reducing the dose to 0.6mg twice daily.
If you are using Colchicine prophylactically your dose is 0.6mg daily or twice daily. Usually, the dose is kept lower to reduce the possibility of GI side effects. Colchicine is not intended to be used long term as it serves more as a bridge before you are placed on a longer term therapy .You stay on this medication for about 3-6 months until your urate level have stabilized.
If you have kidney disease, your health care provider will adjust the dose of the medication. The side effects of colchicine for some individuals are GI in nature: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
Another medication which can be used are steroids. The steroids (Prednisone, prednisolone, methylprednisolone) can be given in form of pills. If other interventions are ineffective or contraindicated steroids can be injected into a single joint.
Long term strategies with medications.
Here there are two choices Allopurinol(brand names are Alloprim, Zyloprim) and febuxostat ( brand names are Uloric, Adenuric).
Allopurinol works by reducing the amount of urate produced in your body. The usual recommendation is to continue with this medication indefinitely as sometimes stopping the medication can lead to a recurrence of gout. The goal is for your serum urate level to be less than 6.0 mg/dl and in patients who have tophi less than 5.0mg/dl. If you have kidney problems the starting dose of Allopurinol will be adjusted by your healthcare provider. The starting dose for febuxostat is 40mg daily, it can be increased to 80 mg daily if your goal urate levels are not reached.
Other medications (I am listing them to the side) which can be used are Probenecid, Lesinurad and Pegloticase. All of them have urate lowering properties and have specific indications.
Fourteen Lifestyle changes to crush gout!
Every single study associated with these tips are listed in the description for further reading.
- Weight loss is encouraged, as obesity is a risk factor. Just losing weight has shown to lower uric acid levels (3)(4)
- Cut out or limit intake of sugary drinks (6)
- Stop any medications which can provoke gout like thiazide diuretics
- Earlier in this article I mentioned if you ingest purine rich foods you are at a risk for a gout attack. The advice will be to reduce or avoid these foods. (5)(15)
- The approach nowadays is to follow a healthier diet, plant-based diet rich in vegetables and fruits, whole grains, reduced saturated fat and lean source of meat such as chicken or turkey. Yes, there is research to show the certain vegetables which are high in purines such as spinach or asparagus DO NOT increase having gout attacks (6)(15)
- Encourage the intake of water
- Intake of low-fat dairy products in the context of a DASH diet has been shown to be helpful in lowering uric acid levels(11)(12)
- Studies have shown that Vitamin C lowered uric acid levels. Vitamin rich foods such as citrus fruits, peppers, and strawberries (8)
- Intake of cherries has been associated with decreased gout attacks (7)
- Intake of dietary and supplemental omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids have also shown to decrease uric acid levels(9)
- Dietary fiber and folate , yes that helps too(10)
- Following the DASH diet (dietary approach to stop hypertension) a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low fat dairy products is also encouraged to manage your gout(11)
- It goes without saying to avoid or minimize alcohol intake (14)
- There has been some research to suggest drinking coffee is beneficial in lowering uric acid levels Please take in coffee in moderation. (13)
Check YouTube video here.
Have a good day and Think your Health.
Sources::
4) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
5) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
6) https://ard.bmj.com/content/
7) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/
9) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
10) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
11) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
12) https://www.healthline.com/
13) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
14) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/.
15) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15014182/