Frontotemporal demetia FTD) is a form of dementia which affects the front of your brain and the side of your brain.
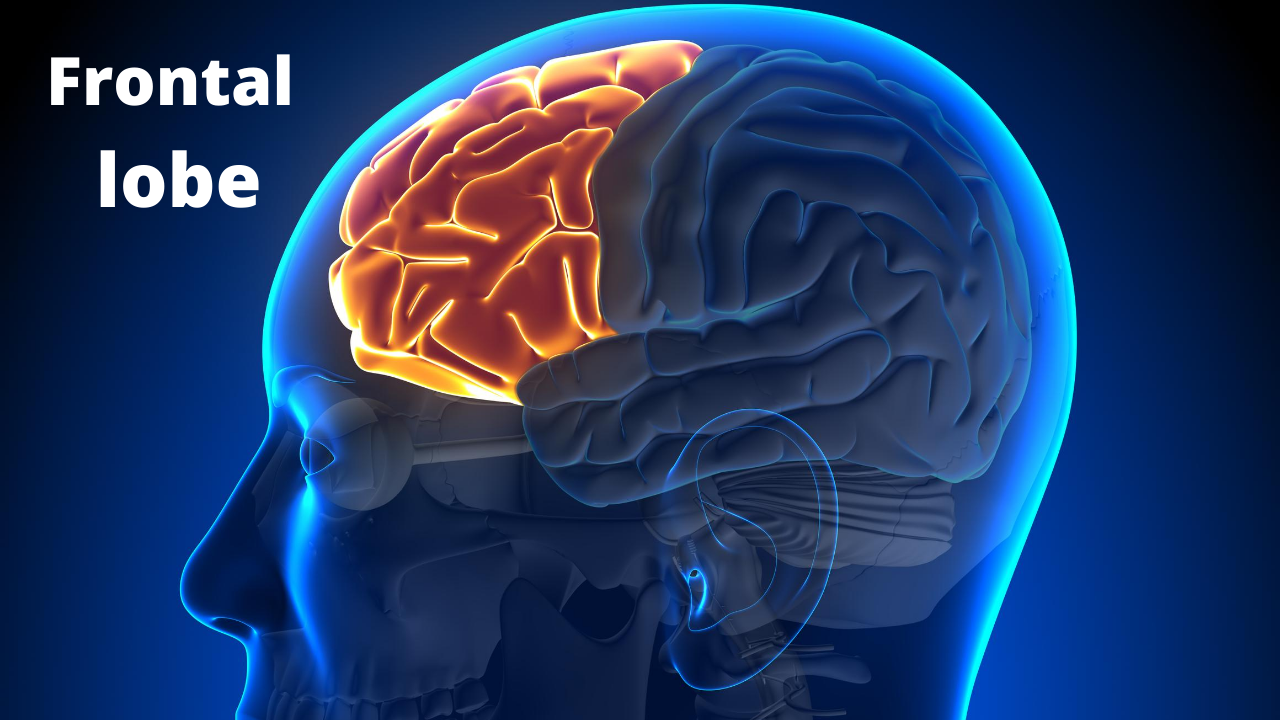
The frontal lobe is located in the front of the brain and the temporal lobe is located in the side of the brain. The frontal lobe has many functions, and I will touch on some I want to highlight.

The frontal lobe helps put thoughts into words. So, damage to a specific area in the frontal lobe called Broca’s region affects speech and the ability to understand language. It also has some role in forming long term memory. It plays a role in forming your personality. Therefore, damage to this area affects someone’s personality. Some of your loved ones might who had been previously reserved individuals might be acting up, or there might be loss of inhibition with hypersexual behavior. Motors kills can also be affected if the frontal lobe is damaged, the skills that control voluntary movements such as walking and running. The Frontal lobe is important for empathy and you might discover that your loved one is not reacting in an usual manner or there are in fact indifferent. The frontal lobe tells you that you are sitting in a particular place( imagine you are sitting on a chair while reading this), it helps you plan and organize complex tasks. If the frontal lobe is damaged these are all affected.
The temporal lobe plays role in encoding memory as well as processing auditory information. The temporal lobes also have a role in language processing as well as processing of our emotions.
What is the typical age for this type of dementia?
FTD is a common cause of early-onset dementia. And usually occurs around the age of 60. It has been reported as early as in the twenties and as late as in the nineties.
Are there different types of FT s dementia?
Yes, in fact there are 3. I just think that you should be aware of them.
Treatment and approach does not change. The 3 types are: behavioral variant FTD and two forms of primary progressive aphasia (PPA), nonfluent variant PPA and semantic variant PPA.
What causes FT dementia?
Frontotemporal dementia is caused by clumps of abnormal protein called tau forming inside brain cells. They damage the brain cells and stop them from working. The brain cells are then not able to communicate with each other.
Other risk factors are family history and genetics.
What is the difference between dementia and FT dementia and the most common dementia Alzheimer’s dementia?
There are many different types of dementia and distinguishing is important to establish a diagnosis and prognosis depending on the type of dementia. The choice of medication can be different to help with symptom management of different types of dementia. When I talk about the different dementia, this is a very general and global term. The analogy I draw is pain. Pain is also very general term, but there are different types of pain such as your muscle pain, stomach pain, headaches. All these different types of pain are different. Similarly, there are different types of dementia..
What are the symptoms of FT dementia?
I will mainly speak about the behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia:
There are social inappropriate behaviors such touching strangers, urinating in public or rude and offensive remarks, taking away objects or items.
Similarly, to young toddlers they might place objects in their mouths. Sometimes they fill up their mouths with food and not chew. Food cravings might change as they may have a liking for very sweet foods.

Some behaviors can be repetitive and even stereotypical such as constantly cleaning or hoarding. Hiding items. Constantly checking. Some of your loved ones might have very rigid routines which they do not want to change, which can be extremely tiresome and frustrating for caregivers.
Some patients lose empathy with lack of motivation and regressing and becoming extremely passive. This type of apathy can be often mistaken for depression.
About 20% of patients also develop a motor neuron disease, affecting overall function and movement.
One sentence on the other variant which is PPA: primary progressive aphasia. This variant is characterized early loss of language with episodic preservation of overall cognition.
How do we diagnose FT dementia?
The diagnosis is made clinically, and other testing is done to help also exclude other disease entities.
The diagnosis is based on physical examination in particular a neurological examination. Your Doctor might order blood tests to exclude other organic causes such as B12 deficiency. He or she might order neuropsychological testing early in the course of the disease to evaluate executive function. Neuroimaging tests such as a brain scans such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and glucose positron emission scans are tests to help exclude structural pathology.
Prognosis and treatment:
Usually this is around 8-10 years from the time of symptoms onset, the behavioral variant has a shorter prognosis, especially if they have the motor variant of the disease than the prognosis is less than 2 years.
Unfortunately, there are no curative drugs. Non-pharmacological approach is emphasized and will need different care teams members in the coordination of care such as PT/OT, SW and behavior therapist, nurse and home care nurses, dietitians and home health aides. There are specialized organizations and associations who can help with this coordination of care. There are medications which can help with symptom management; however, they should only be used if non-pharmacological ways and approaches have been exhausted.
Have a good day and Think your Health.See entire video here: FT dementia
Sources:






